Look around you. Whether you’re at home, in your car, or walking through a city, an engineering marvel is quietly at work, ensuring safety, efficiency, and functionality. This marvel is the flexible stainless steel hose. Far more than just a simple tube, it is a critical component designed to solve one of engineering’s oldest challenges: how to connect two points that move, vibrate, or get hot.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel the world of flexible metal hoses. We’ll explore what they are, why they’re so indispensable across countless industries, and what you need to know to choose the right one for your application.
What Exactly is a Flexible Stainless Steel Hose?
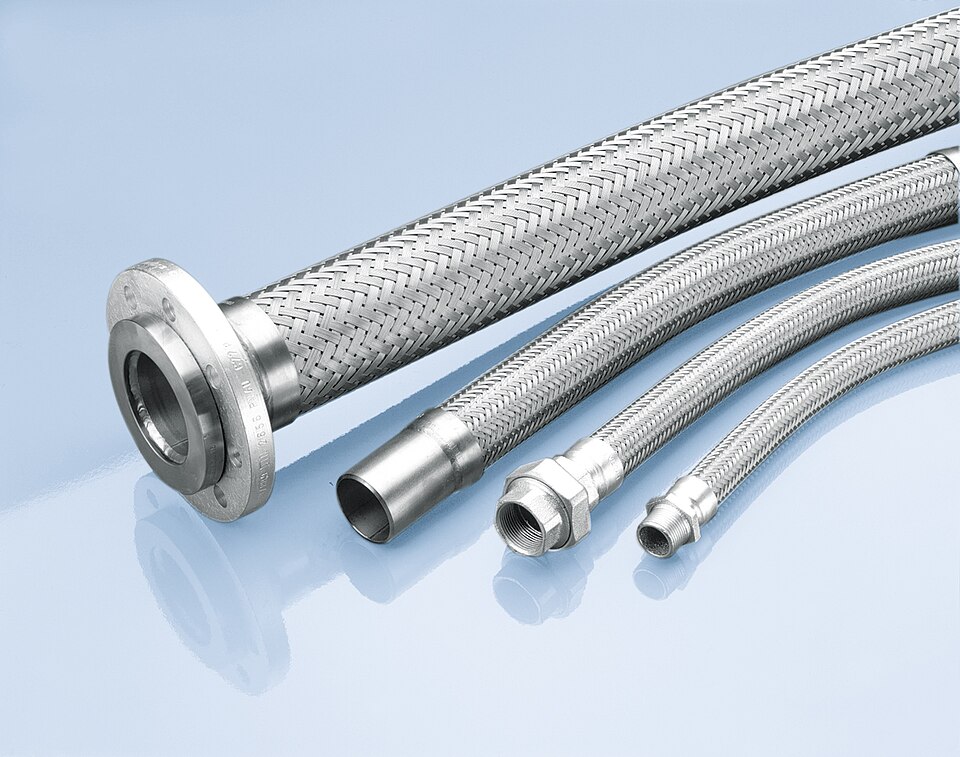
At its core, a flexible stainless steel hose is a versatile conduit designed to transport liquids, gases, vapors, and even solids in a wide range of temperatures and pressures. Unlike a rigid pipe, it is engineered to accommodate movement, absorb vibration, and compensate for misalignment.
Its construction is a masterpiece of engineering:
-
The Corrugated Core: The inner tube is corrugated, creating a series of concentric ridges and valleys. This corrugation is the secret to its flexibility, allowing it to bend, compress, and extend without kinking or collapsing.
-
The Braided Shield: Surrounding the core is a braided sheath, typically made from stainless steel wire. This braid is not for flexibility but for containment and strength. It acts as a pressure-bearing layer, reinforcing the hose and protecting it from over-extension and external damage.
-
The End Fittings: The hose is terminated with fittings—often made from stainless steel, brass, or other alloys—that are securely attached (usually via crimping or welding) to allow for a leak-tight connection to pipes, valves, or equipment.
Why Stainless Steel? The Unbeatable Advantages
The choice of material is no accident. Stainless steel, particularly grades 304 and 316, provides a suite of properties that make these hoses unparalleled in performance.
-
Exceptional Durability and Longevity: Stainless steel is incredibly strong and resistant to mechanical damage like abrasion, crushing, and impact. A properly specified hose can last for decades, even in harsh conditions.
-
Superior Temperature Resistance: These hoses can handle extreme thermal cycling, from cryogenic temperatures up to 1000°F (538°C) and beyond, depending on the construction. They won’t melt, warp, or degrade under heat stress.
-
High-Pressure Capability: The combination of the corrugated core and the braided sheath creates a structure that can contain very high internal pressures, making them essential in hydraulic systems and industrial processing.
-
Outstanding Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel naturally resists rust and corrosion from water, chemicals, and atmospheric exposure. Grade 316 offers even greater resistance, especially to chlorides, making it ideal for marine and chemical applications.
-
Ultimate Flexibility and Movement: They are designed to flex millions of times without failure. This makes them perfect for applications with constant vibration (like pumps and compressors) or thermal expansion (like steam lines).
-
Safety and Containment: The braided construction provides a critical safety factor, containing fluids and gases should the inner core fail, and protecting against leaks that could lead to fire, environmental damage, or injury.
A World of Applications: Where You’ll Find Flexible Metal Hoses
The versatility of these hoses means they are hidden in plain sight, powering countless industries.
-
Industrial & Manufacturing: Transporting steam, chemicals, solvents, and fuels. Connecting pumps, compressors, and engines to absorb vibration.
-
HVAC & Refrigeration: Used as vibration eliminators on chillers, condensers, and compressors. They handle the transfer of refrigerants and accommodate the thermal expansion and contraction of system components.
-
Automotive & Aerospace: In vehicles, they are used in power steering, brake lines, and turbocharger systems. In aerospace, they handle critical fuel, hydraulic, and air systems.
-
Electrical & Semiconductor: Protecting delicate electrical wiring and fiber optic cables in cable management systems, providing flexibility and EMI/RFI shielding.
-
Food, Beverage & Pharmaceutical: Sanitary-grade hoses with polished interiors are used to transfer ingredients, dairy, beverages, and pharmaceuticals, meeting strict FDA and USDA hygiene standards.
-
Residential & Commercial: You’ll find them connecting gas lines to stoves and dryers, serving as supply lines for water heaters and toilets, and even in appliance internal components.
Not All Hoses Are Created Equal: Key Types to Know
Understanding the different constructions is key to selecting the right hose.
-
Interlocked Hoses: Feature a helical, interlocked strip of steel. They are very rigid and used primarily for protection of wires and cables, or as ducting for light materials. They are not typically pressure-tight.
-
Corrugated Hoses: The true workhorse for pressure applications. They can be single-ply (with one braid) for medium pressure or double-ply (with two braids) for higher pressure and added safety.
-
P&T Rated Hoses: These are Pressure and Temperature Rated hoses. They are manufactured to specific standards (like SAE) and have clearly marked maximum working pressure and temperature limits. Never use a non-rated hose for a critical pressure application.
Choosing the Right Hose: A 5-Point Checklist
Selecting the wrong hose can lead to failure, downtime, and danger. Always consider these five factors:
-
Media Compatibility: What will flow through the hose? Ensure the stainless steel grade and any internal lining are chemically compatible with the fluid to prevent corrosion from the inside out.
-
Temperature Range: What are the minimum and maximum temperatures the hose will experience? Both the media temperature and the ambient temperature matter.
-
Pressure Requirements: Know your system’s working pressure and any potential pressure spikes (water hammer). Always choose a hose with a maximum working pressure (MWP) that exceeds your system’s requirements.
-
Size and Length: Specify the correct inner diameter (ID) for flow requirements and the length needed to accommodate the movement without being over-stretched or compressed.
-
End Connections: The fittings must match the thread type (NPT, BSP), size, and gender of the ports you are connecting to. Material compatibility is also crucial here.
Installation and Maintenance: Best Practices
Even the best hose will fail if installed incorrectly.
-
Never Over-Bend: Every hose has a minimum bend radius. Bending it tighter than this can kink and damage the core.
-
Avoid Torque: Do not twist the hose during installation. It is designed to flex, not to be rotated.
-
Inspect Regularly: Look for signs of wear, such as broken wires in the braid, kinks, corrosion, or damage to the end fittings. Replace hoses at the first sign of deterioration.
Conclusion: The Flexible Backbone of Modern Engineering
The flexible stainless steel hose is a testament to the idea that the simplest solutions are often the most brilliant. By mastering the principles of flexibility, strength, and durability, it solves complex problems in virtually every field of engineering. From the water line behind your wall to the fuel line in a jet engine, this unassuming component works tirelessly to keep our world connected, safe, and in motion. By understanding its capabilities and choosing wisely, you ensure your systems run smoothly and reliably for years to come.